A plate heat exchanger is used to transfer heat energy from one fluid to another. These fluids never encounter each other due to being separated by the heat exchanger.
A plate heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that uses metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids. This has a major advantage over a conventional heat exchanger in that the fluids are exposed to a much larger surface area because the fluids are spread out over the plates.
Different types of plate heat exchanger have many potential applications. This includes pasteurizers, beverage processing, connectors between chillers, boilers, and cooling towers, and other process engineering applications. The plates are often spaced by rubber sealing gaskets which are cemented into a section around the edge of the plates. The plates are pressed to form troughs at right angles to the direction of flow of the liquid which runs through the channels in the heat exchanger.

The corrugation on the plates drives the fluid on a tortuous path, creating a distance from 1 to 5 millimeters between two adjacent plates.
The fluids can pass through the channels in series (a less common solution) or parallel by making counter-flow configurations.
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between two or more fluids. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes.
Heat transfer to highly viscous or sticky materials is needed in certain applications. A scraped surface heat exchanger is the best option for providing efficient heat transfer in such applications because the scraping blades prevent the product from accumulating on the internal surfaces.
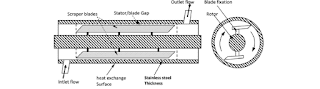
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_exchanger#Dynamic_scraped_surface_heat_exchanger
https://www.linquip.com/blog/plate-heat-exchanger/
https://www.linquip.com/blog/types-of-plate-heat-exchanger/
https://www.linquip.com/blog/working-principle-plate-heat-exchanger/
https://www.linquip.com/blog/scraped-surface-heat-exchanger/


















 Differences Between forwarding and Survey Reverse Biasing and Linear Potentiometer
Differences Between forwarding and Survey Reverse Biasing and Linear Potentiometer What is Drift Eliminator 101 ?
What is Drift Eliminator 101 ?